Complete Medical Guide and Prevention for Heart Diseases Volume VII; Atrial Fibrillation
Nonfiction, Health & Well Being, Health, Ailments & Diseases, Heart, Health Care Issues| Author: | Medical Professionals | ISBN: | 1230000037082 |
| Publisher: | MedHealth | Publication: | December 6, 2012 |
| Imprint: | Language: | English |
| Author: | Medical Professionals |
| ISBN: | 1230000037082 |
| Publisher: | MedHealth |
| Publication: | December 6, 2012 |
| Imprint: | |
| Language: | English |
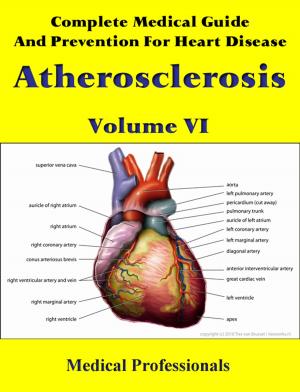
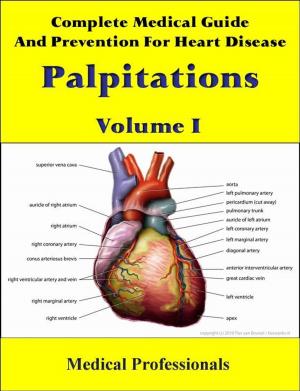
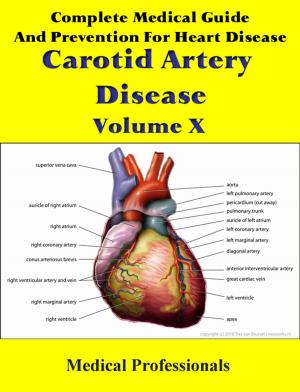
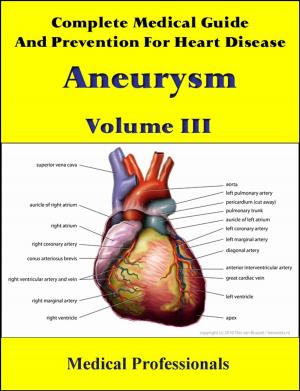
Atrial fibrillation (AF or A-fib) is the most common cardiac arrhythmia (irregular heart beat). It may cause no symptoms, but it is often associated with palpitations, fainting, chest pain, or congestive heart failure. However, in some people atrial fibrillation is caused by otherwise idiopathic or benign conditions.
AF increases the risk of stroke; the degree of stroke risk can be up to seven times that of the average population, depending on the presence of additional risk factors (such as high blood pressure). It may be identified clinically when taking a pulse, and the presence of AF can be confirmed with an electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG) which demonstrates the absence of P waves together with an irregular ventricular rate.
In AF, the normal regular electrical impulses generated by the sinoatrial node are overwhelmed by disorganized electrical impulses usually originating in the roots of the pulmonary veins, leading to irregular conduction of impulses to the ventricles which generate the heartbeat. AF may occur in episodes lasting from minutes to days ("paroxysmal"), or be permanent in nature. A number of medical conditions increase the risk of AF, particularly mitral stenosis (narrowing of the mitral valve of the heart).
Atrial fibrillation may be treated with medications to either slow the heart rate to a normal range ("rate control") or revert the heart rhythm back to normal ("rhythm control"). Synchronized electrical cardioversion can be used to convert AF to a normal heart rhythm. Surgical and catheter-based therapies may be used to prevent recurrence of AF in certain individuals. People with AF often take anticoagulants such as warfarin to protect them from stroke, depending on the calculated risk. The prevalence of AF in a population increases with age, with 8% of people over 80 having AF. Chronic AF leads to a small increase in the risk of death. A third of all strokes are caused by AF.
Contents
Atrial fibrillation (AF or A-fib) is the most common cardiac arrhythmia (irregular heart beat). It may cause no symptoms, but it is often associated with palpitations, fainting, chest pain, or congestive heart failure. However, in some people atrial fibrillation is caused by otherwise idiopathic or benign conditions.
AF increases the risk of stroke; the degree of stroke risk can be up to seven times that of the average population, depending on the presence of additional risk factors (such as high blood pressure). It may be identified clinically when taking a pulse, and the presence of AF can be confirmed with an electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG) which demonstrates the absence of P waves together with an irregular ventricular rate.
In AF, the normal regular electrical impulses generated by the sinoatrial node are overwhelmed by disorganized electrical impulses usually originating in the roots of the pulmonary veins, leading to irregular conduction of impulses to the ventricles which generate the heartbeat. AF may occur in episodes lasting from minutes to days ("paroxysmal"), or be permanent in nature. A number of medical conditions increase the risk of AF, particularly mitral stenosis (narrowing of the mitral valve of the heart).
Atrial fibrillation may be treated with medications to either slow the heart rate to a normal range ("rate control") or revert the heart rhythm back to normal ("rhythm control"). Synchronized electrical cardioversion can be used to convert AF to a normal heart rhythm. Surgical and catheter-based therapies may be used to prevent recurrence of AF in certain individuals. People with AF often take anticoagulants such as warfarin to protect them from stroke, depending on the calculated risk. The prevalence of AF in a population increases with age, with 8% of people over 80 having AF. Chronic AF leads to a small increase in the risk of death. A third of all strokes are caused by AF.
Contents