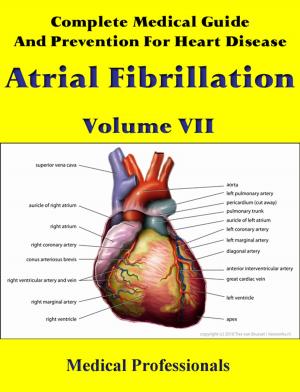
DASH Diet Plan: Your Guide to Lowering High Blood Pressure With 7 Days Program
Nonfiction, Health & Well Being, Health, Ailments & Diseases, Heart, Nutrition & Diet, Diets| Author: | National Health Institute | ISBN: | 1230000030306 |
| Publisher: | MedHealth | Publication: | November 12, 2012 |
| Imprint: | Language: | English |
| Author: | National Health Institute |
| ISBN: | 1230000030306 |
| Publisher: | MedHealth |
| Publication: | November 12, 2012 |
| Imprint: | |
| Language: | English |
The DASH diet (Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension) is a dietary pattern promoted by the U.S.-based National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (part of the National Institutes of Health, an agency of the United States Department of Health and Human Services) to prevent and control hypertension. The DASH diet is rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and low-fat dairy foods; includes meat, fish, poultry, nuts and beans; and is limited in sugar-sweetened foods and beverages, red meat, and added fats. In addition to its effect on blood pressure, it is designed to be a well-balanced approach to eating for the general public. It is now recommended by the US Department of Agriculture (USDA) as an ideal eating plan for all Americans.[citation needed]
The DASH diet is based on NIH studies that examined three dietary plans and their results. None of the plans were vegetarian, but the DASH plan incorporated more fruits and vegetables, low fat or nonfat dairy, beans, and nuts than the others studied. Not only does the plan emphasize good eating habits, but also suggests healthy alternatives to "junk food" and discourages the consumption of processed foods. The NIH has published a guidebook, "Your Guide to Lowering your Blood Pressure With DASH", which details the nutrition facts of popular mainstream food items and their healthy alternatives. The manual also provides samples of meal plans and proportions along with their associated nutritional information. The last pages of the manual provides a list of resources and how to obtain them.
The diet reduced systolic blood pressure by 6 mm Hg and diastolic blood pressure by 3 mm Hg in patients with high normal blood pressure, now called "pre-hypertension." Those with hypertension dropped by 11 and 6, respectively. These changes in blood pressure occurred with no changes in body weight. The DASH dietary pattern is adjusted based on daily caloric intake ranging from 1699 to 3100 dietary calories.
The DASH diet (Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension) is a dietary pattern promoted by the U.S.-based National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (part of the National Institutes of Health, an agency of the United States Department of Health and Human Services) to prevent and control hypertension. The DASH diet is rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and low-fat dairy foods; includes meat, fish, poultry, nuts and beans; and is limited in sugar-sweetened foods and beverages, red meat, and added fats. In addition to its effect on blood pressure, it is designed to be a well-balanced approach to eating for the general public. It is now recommended by the US Department of Agriculture (USDA) as an ideal eating plan for all Americans.[citation needed]
The DASH diet is based on NIH studies that examined three dietary plans and their results. None of the plans were vegetarian, but the DASH plan incorporated more fruits and vegetables, low fat or nonfat dairy, beans, and nuts than the others studied. Not only does the plan emphasize good eating habits, but also suggests healthy alternatives to "junk food" and discourages the consumption of processed foods. The NIH has published a guidebook, "Your Guide to Lowering your Blood Pressure With DASH", which details the nutrition facts of popular mainstream food items and their healthy alternatives. The manual also provides samples of meal plans and proportions along with their associated nutritional information. The last pages of the manual provides a list of resources and how to obtain them.
The diet reduced systolic blood pressure by 6 mm Hg and diastolic blood pressure by 3 mm Hg in patients with high normal blood pressure, now called "pre-hypertension." Those with hypertension dropped by 11 and 6, respectively. These changes in blood pressure occurred with no changes in body weight. The DASH dietary pattern is adjusted based on daily caloric intake ranging from 1699 to 3100 dietary calories.